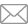
DHC.2 BEAVER
The Beaver is a highly successful STOL utility transport, used by military and civilian operators for moving personnel and cargo (especially in remote areas), search and rescue operations and crop dusting. De Havilland designers led by Phil Garratt with chief engineer W. 'Jaki' Jakimiuk and aerodynamicist Z. 'Steppy' Stepniewski in 1946 set on designing a robust plane with STOL characteristics, which could answer the needs of Canadian aviators flying in difficult conditions of the country's vast interior.
On 16 August 1947 the plane made its maiden flight. It was a high-wing monoplane of all-metal construction powered by a radial engine. It could be equipped with wheels, skids or floats, enabling operations in various conditions. Large doors installed on either side of the fuselage allowed easy loading of cargo, including oil drums. The plane had a payload of 2,100 lb (953 kg) and could carry 6 passengers.
Over 1,600 examples had been built when the production ceased in 1967 and many were exported abroad. The United States Army became one of the major operators. Hundreds of Beavers are still flying and the plane is considered to be one of Canada's top engineering achievement of the 20th century.
Specifications (DHC. 2 Beaver Mk 1)
wingspan: 48 ft 0 in (14.63 m)
length: 30 ft 3 in (9.22 m)
max. takeoff weight: 5,100 lb (2,313 kg)
max. speed: 158 mph (255 km/h)
ceiling: 18,000 ft (5,486 m)
range: 455 miles (732 km)
powerplant: Pratt & Whitney R-985 Wasp Jr. radial engine rated at 450 hp (336 kW)